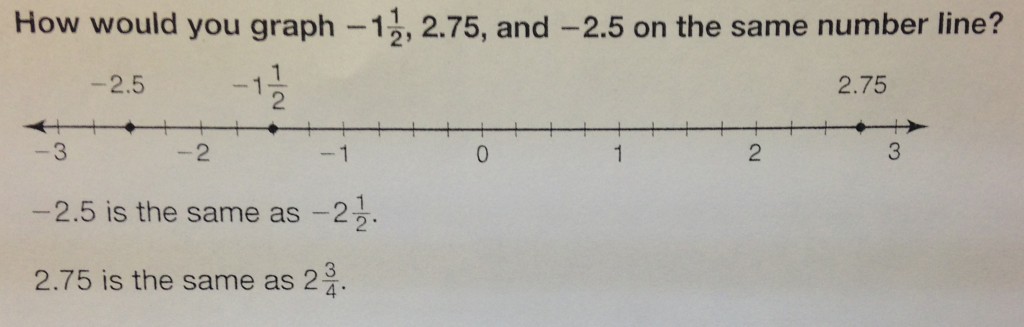04-Understanding Rational Numbers
We can compare and order fractions. We can compare and order fractions. We can also compare and order integers. Rational numbers basically takes all of these concepts and throws them into one lesson.
A rational number is any number that can be made by dividing two integers. Another way to think of it, is any number you could place on a number line. This includes whole numbers, integers both positive and negative, positive and negative fractions, and positive and negative decimals. It is possible to graph all of these on the same number line.
Example:
Remember, with fractions, -2.5 is in between -3 and -2, so make sure it gets put in the correct place. A common mistake make would be putting it to the right of -2, because that’s what you would do with postivie numbers. Be sure to not make this mistake. It goes to the left of -2 and to the right of -3.
Honestly, the easiest way to graph, compare or order any rational numbers is to make sure they are all in the same form. Don’t try to compare fractions to decimals, convert them so they are either both fractions or both decimals. Beyond that, they follow the same rules.
- On a number line, the numbers further to the left are lesser, and the numbers further to the right are greater.
- When comparing positive and negative numbers, positive numbers are always greater.
- When comparing positive numbers, the larger number is greater.
- When comparing negative numbers, the smaller number is greater, even with fractions and decimals.